Computer Accessibility refers to the user-friendliness of a computer system for all, regardless of their disability. It enables a person with a disability or impairment to use a computer. It is known as Assistive Technology.
Launching Accessibility Options :
To launch accessibility options in WindowsXP, Click Start > Control Panel > Accessibility Options.
Various tabs in the Accessibility Option Window :
Keyboard Tab to configure accessibility options for the Keyboard is displayed.
1) Sticky Keys: Sticky Keys is an accessibility feature to help computer users with physical disabilities, but it is also used by others as a means to reduce repetitive strain. StickyKeys allows the user to press and release a modifier key, such as Shift, Ctrl, Alt, or the Windows key, and have it remain active until any other key is pressed.
2) Filter Keys: It is an accessibility function that tells the keyboard to ignore brief or repeated keystrokes, making typing easier for people with hand tremors.
3) ToggleKeys: It is an accessibility function that is designed for people who have vision impairment or cognitive disabilities. When ToggleKeys is turned on, the computer emits sound cues when the locking keys (Caps Lock, Num Lock, or Scroll Lock) are pressed.
Sound Tab to configure accessibility options for sound is displayed.
1) SoundSentry: SoundSentry is designed to help users with auditory impairments. SoundSentry generates visual warnings, such as a blinking title bar or a flashing border, whenever the computer generates a sound.
2) ShowSounds: ShowSounds instructs applications that convey information by sound, to also provide information visually, through text captions or informative icons.
Display Tab to configure accessibility options for Display is displayed.
1) High Contrast: High Contrast is an accessibility feature to assist people with vision impairment. You can change the size and color of fonts and the background for ease of viewing.
2) Cursor Options: Cursor Options is an accessibility feature that assists people with vision impairment
by changing the blink rate and width of the cursor.
Mouse Tab to configure accessibility options for Mouse is displayed.
1) MouseKeys: MouseKeys is an accessibility feature that assists people who have difficulty using a mouse. This option uses the keyboard (especially a numeric keypad) as a pointing device instead of a mouse. Use number key 4 to move left, 6 to move right, 2 to move down and 8 to move up.
General Tab: enables you to configure accessibility options for all users. This tab enables you to configure accessibility options for all users. Select the General tab, and a window to configure additional accessibility options will be displayed.
“Turn off accessibility features after idle for”,
“Give a warning message when turning a feature on”
Serial Keys: Serial Keys is an accessibility feature that assists people that have difficulty using a keyboard or a mouse (or both). They can use special devices such as Sip, Puff, and Breath Switches to provide input to the computer through Serial Ports. For example, sipping on the tube activates one
device, while puffing on the same tube activates another.
https://youtu.be/o_ICinwfN6g
MCQ - Session 1: Working with accessibility options
1. Computer ___________ refers to the user friendliness of a computer system for all, regardless of their disability.
a. Shortcut Keys
b. Accessibility
c. Ctrl & Alt Key
d. None of the above
Hide Answer ⟵
2. What are the different type of impairments that impact computer usage?
a. Dyslexia
b. Visual Impairment
c. Hearing Impairment
d. All of the above
Hide Answer ⟵
3. Accessibility options are available in __________.
a. Setting
b. Control Panel
c. Desktop
d. None of the above
ANS:b. Control Panel
4. ___________ is an accessibility feature to help computer users with physical disabilities, but it is also used by others as a means to reduce repetitive strain.
a. Filter keys
b. Toggle Keys
c. Sticky Keys
d. None of the above
Hide Answer ⟵
5. _________ enables the user to hold and release a modifier key, like as Shift, Ctrl, Alt, or the Windows key, and have it remain active until another key is pressed.
a. Filter keys
b. Toggle Keys
c. Sticky Keys
d. None of the above
Hide Answer ⟵
6. The __________accessibility function instructs the keyboard to ignore short or repeated inputs, making typing simpler for those people who have hand tremors.
a. Filter keys
b. Toggle Keys
c. Sticky Keys
d. None of the above
Hide Answer ⟵
7. __________ is an accessibility feature for persons with vision impairment or cognitive problems.
a. Filter keys
b. Toggle Keys
c. Sticky Keys
d. None of the above
8. _________ is turned on, the computer emits sound cues when the locking keys such as Caps lock, Num lock and Scroll lock are pressed.
a. Filter keys
b. Toggle Keys
c. Sticky Keys
d. None of the above
Hide Answer ⟵
9. ___________ is designed to help users with auditory impairments.
a. Filter keys
b. Toggle Keys
c. Sound Sentry
d. None of the above
Hide Answer ⟵
10. When the computer makes a sound, ________ produces visual effects such as a blinking title bar or a flashing border.
a. Filter keys
b. Toggle Keys
c. Sound Sentry
d. None of the above
Hide Answer ⟵
11. ___________ directs applications that provide information through sound to also give information visually, through written captions or informative icons.
a. Filter keys
b. Show Sound
c. Sound Sentry
d. None of the above
Hide Answer ⟵
12. ___________ is an accessibility feature to assist people with vision impairment. You can change the text size and color, as well as the background color, to make it easier to read.
a. High Contrast
b. Show Sound
c. Sound Sentry
d. None of the above
Hide Answer ⟵
13. _____________ is also an accessibility feature that assists people with vision impairment by changing the blink rate and width of the cursor.
a. High Contrast
b. Cursor Options
c. Sound Sentry
d. None of the above
Hide Answer ⟵
14. The ____________option uses the keyboard (especially numeric keypad) as a pointing device instead of a mouse.
a. High Contrast
b. Mouse key
c. Sound Sentry
d. None of the above
Hide Answer ⟵
15. ____________ is an accessibility feature that assists people that have difficulty using a keyboard or a mouse (or both). They can use special devices such as Sip, Puff and Breath Switches to provide input to the computer through Serial Ports.
a. High Contrast
b. Mouse key
c. Serial Keys
d. None of the above
Hide Answer ⟵
16. The option in Microsoft Windows XP used for helping users with physical disabilities and to reduce repetitive strain is ____________________.
a. Toggle Key
b. Sticky Key
c. Tab Key
d. None of the above
Hide Answer ⟵
17. Sound Sentry is intended to assist users who have ____________ disabilities.
a. Auditory Impairments
b. Cognitive Impairments
c. Visual Impairments
d. Dexterity Impairments
Hide Answer ⟵
18. The High Contrast feature in Microsoft Windows XP is designed to help persons who have _______________ impairments.
a. Auditory Impairments
b. Cognitive Impairments
c. Visual Impairments
d. Dexterity Impairments
Hide Answer ⟵
19. ___________________ is designed to assist people that have difficulty using a keyboard or a mouse.
a. KeyboardKeys
b. MouseKeys
c. TabKeys
d. GeneralKeys
Hide Answer ⟵
SESSION 2: NETWORKING FUNDAMENTALS
A computer network is a collection of computers and other hardware components interconnected by communication channels (cables or satellites) that allow sharing of resources and information.
Networks are designed using the following architecture:
1) Peer-to-Peer Architecture: Networks in which all computers have an equal status are called peer-to-peer networks. Generally in such a network, each terminal has an equally competent CPU.
2) Client-Server Architecture: Networks in which certain computers have special dedicated tasks, providing services to other computers (in the network) are called client-server networks. The computer(s) which provide services are called servers and the ones that use these services are called clients.
TYPES OF NETWORKS :
1) Local Area Network: A local area network (LAN) is one that connects computers and devices in a limited geographical area such as a home, school, computer laboratory, or office building.
2) Metropolitan Area Network: A Metropolitan Area Network (MAN) is one that connects computers and devices in a single city or a town.
3) Wide Area Network: A wide area network (WAN) is one that covers a broad area (i.e., any network that links across metropolitan, regional, or national boundaries).
Internet :
The Internet is a global system of interconnected computer networks that use the standard Internet protocol suite to serve billions of users worldwide. It is a network of networks.
Uses of the Internet:
- Internet is used by students, and educational institutes to gather information for research.
- It is used for online shopping.
- It is used for sending and receiving mail.
- It is used for playing games.
- It is used for Online Transactions.
World Wide Web: World Wide Web (abbreviated as WWW or W3, commonly known as the Web), is a
system of interlinked hypertext documents accessed via the Internet.
A hypertext document contains links referring to other parts of the document, or even to whole other documents..
Advantages of Networking :
1) Data Sharing: Networking allows the sharing of data.
2) Files Transfer: One User can send text files, spreadsheets, etc. to other users.
3) Hardware Sharing: Hardware components such as printers, scanners, etc. can also be shared.
4) Internet Access Sharing: You can purchase a single Internet connection and share it among other computers in a network
Web Browser: A Web Browser is software used to view Web sites and acts as an interface between the user and the World Wide Web.
Web Server: A web server is a computer that stores websites and their related files for viewing on the Internet.
Internet Service Provider: An Internet service provider (ISP) is an organization that provides you with access to the Internet via a dial-up (using a modem) or direct (hard wired) or wireless connection. for example Bharat Sanchar Nigam Limited (BSNL), Airtel, MTS, Vodafone, Tata Docomo, etc.
Modem: A modem is a device that converts digital computer signals into a form (analog signals)
that can travel over phone lines. It also re-converts the analog signals back into digital
signals. The word modem is derived from its function MOdulator/DEModulator.
Types of Common Internet Connectivity: There are different types of Internet Connectivity available today; it can be widely categorized into wired and wireless access.
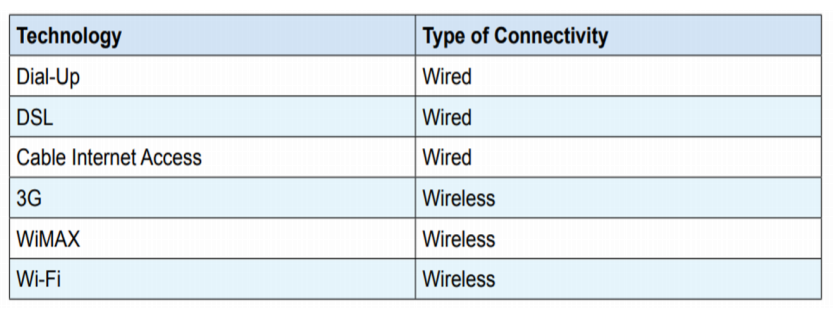
1) Dial-up: Dial-up Internet access is a form of Internet access that uses the facilities of the
public switched telephone network (PSTN) to establish a connection to an Internet service
provider (ISP) via telephone lines using a device called MODEM. Users dial a particular number
provided by the ISP and gain access to the Internet. These connections are extremely slow and in most cases, it is replaced by a high-speed connection such as DSL or Cable Modem.
2) DSL: Digital subscriber line(DSL) provides Internet access by transmitting digital data over wires of a local telephone network. For using a DSL connection, you need a DSL modem and a subscription.

5) WiMAX: WiMAX (Worldwide Interoperability for Microwave Access) is a wireless communications standard designed to provide mobile broadband connectivity across cities and countries through a variety of devices.
6) WI-Fi (Wireless Fidelity): Wi-Fi is a popular technology that allows electronic devices such as computers or mobile phones to exchange data wirelessly over a network, including high-speed
Internet connections.
7) SATELLITE:
DATA TRANSFER ON THE INTERNET
Let’s see what happens to a piece of data, say a Web page when it is transferred over the Internet:
• Each packet is sent from computer to computer until it finds its destination. Each computer on the way decides where next to send the packet. All packets may not take the same route.
• At the destination, the packets are examined. If any packets are missing or damaged, a message is sent asking for them to be re-sent. This continues until all packets have been received intact.
• The packets are now reassembled into their original form. All this is done in seconds!
Session 2: Networking Fundamentals
20. A ______________ is a collection of computers and other hardware components interconnected by communication channels that allow sharing of resources and information.
a. Computer Network
b. Computer Sharing
c. Computer Receiving
d. None of the above
Hide Answer ⟵
21. What are the examples of communication channels _________.
a. Cable Wire
b. Satellites
c. Both a) and b)
d. None of the above
Hide Answer ⟵
22. Example of computer networks architecture __________.
a. Peer – to – Peer architecture
b. Client – Server architecture
c. Both a) and b)
d. None of the above
Hide Answer ⟵
23. Networks in which all computers have an equal status are called __________.
a. Peer – to – Peer Network
b. Client – Server Network
c. Both a) and b)
d. None of the above
Hide Answer ⟵
24. Networks in which certain computers have special dedicated tasks, providing services to other computers are called__________.
a. Peer – to – Peer Network
b. Client – Server Network
c. Both a) and b)
d. None of the above
Hide Answer ⟵
25. The computer provides services called ___________.
a. Client
b. Server
c. Node
d. None of the above
Hide Answer ⟵
26. The computer uses the services which are provided from the server is called __________.
a. Client
b. Server
c. Node
d. None of the above
Hide Answer ⟵
27. What are the major different types of network?
a. Local Area Network
b. Wide Area Network
c. Both a) and b)
d. None of the above
Hide Answer ⟵
28. A ____________ is a network that connects computers and gadgets in a specific geographic area, such as a house, school, computer laboratory, office building, or group of buildings.
a. Local Area Network
b. Wide Area Network
c. Both a) and b)
d. None of the above
Hide Answer ⟵
29. A ______________ network is one which covers a broad area across metropolitan city, regional, or national boundaries.
a. Local Area Network
b. Wide Area Network
c. Both a) and b)
d. None of the above
Hide Answer ⟵
30. The ___________ is a global network of interconnected computer networks that serve billions of people worldwide by utilizing the standard Internet protocol suite.
a. Internet
b. Network
c. Arpanet
d. None of the above
Hide Answer ⟵
31. WWW stands for ___________.
a. Web World Wide
b. World Wide Web
c. World Web Wide
d. None of the above
Hide Answer ⟵
32. WWW is also known as __________.
a. W2
b. W4
c. W3
d. W1
Hide Answer ⟵
33. __________ is a network of interconnected hypertext documents that may be accessed via the Internet.
a. World Wide Web
b. W3
c. Both a) and b)
d. None of the above
Hide Answer ⟵
34. A ________ is a software program that is used to browse Web sites and serves as a bridge between the user and the World Wide Web.
a. World Wide Web
b. Web Server
c. Web Browser
d. None of the above
Hide Answer ⟵
35. What are the advantages associated with networking?
a. Data & File Sharing
b. Hardware Sharing
c. Internet Sharing
d. All of the above
Hide Answer ⟵
36. _________ helps to share hardware components such as printers, scanners etc.
a. Computer Network
b. Hardware Network
c. Information Network
d. None of the above
Hide Answer ⟵
37. ISP stands for ___________.
a. Internet Sharing Provider
b. Internet Services Provider
c. Internet Social Provider
d. All of the above
Hide Answer ⟵
38. Example of Internet Service Provider in India ___________.
a. Bharat Sanchar Nigam Limited
b. Airtel
c. MTS
d. All of the above
Hide Answer ⟵
39. WiMAX stands for ____________.
a. WorldWide Interoperability for Microwave Access
b. WorldWide Interoperability for Micro Access
c. WorldWide Internet for Microwave Access
d. None of the above
Hide Answer ⟵
40. DSL stands for ____________.
a. Dynamic Subscriber Line
b. Digital Subscriber Line
c. Digital Sub Line
d. None of the above
Hide Answer ⟵
41. ISDN stands for ___________.
a. Integrated Services Digital Network
b. Internet Services Dynamic Network
c. Integrated Sub Digital Network
d. Internet Sub Dynamic Network
Hide Answer ⟵
42. Á __________ is a device that converts digital computer signals into analog signals that can travel over phone lines.
a. Router
b. Modem
c. Bridge
d. None of the above
Hide Answer ⟵
43. Modem is also known as ___________.
a. MOdulator/ DEModulator
b. Modular/DeModular
c. Modulate/DeModulate
d. None of the above
Hide Answer ⟵
44. Give the example of a Wired internet connectivity channel?
a. DSL
b. WiMax
c. Wi-Fi
c. All of the above
Hide Answer ⟵
45. Give the example of a Wireless internet connectivity channel?
a. DSL
b. Dial – Up
c. WiMax
d. None of the above
Hide Answer ⟵
46. __________ Internet access is a form of Internet access that uses the facilities of the public switched telephone network (PSTN) to establish a connection to an Internet service provider
a. Dial – up
b. 3G
c. WiMax
d. Wi-Fi
Hide Answer ⟵
47. __________provide Internet access by transmitting digital data over wires of a local telephone network.
a. Dial – Up
b. Digital Subscriber Link (DSL)
c. 3G
d. WiMax
Hide Answer ⟵
48. _________provides wireless communication and mobile broadband connection across cities and countries.
a. WiMax
b. Wi-Fi
c. DSL
d. None of the above
Hide Answer ⟵
49. ___________ is a widely used technology that allows electronic devices as as computers or mobile phones to transmit data wirelessly over a network, including high-speed Internet connections.
a. WiMax
b. Wi-Fi
c. DSL
d. None of the above
Hide Answer ⟵
50. How can we transfer data on the internet?
a. Using Box Switching
b. Using Packet Switching
c. Using Public Switching
d. Using Web Switching
Show Answer ⟶
B.
51. The acronym for LAN is _________________.
a. Large Area Network
b. Last Area Network
c. Local Area Network
d. None of the above
Hide Answer ⟵
52. Three types of Wired Internet Connectivity are ___________ , _________ & ___________.
a. 3G, DSL, Dial-Up
b. Cable Internet Access, DSL, Dial-Up
c. WiMax, 3G, Wi-Fi
d. WiMax, DSL, Dial-up
Hide Answer ⟵
53. Three types of Wireless Internet Connectivity are _________ , ___________ & _________.
a. 3G, DSL, Dial-Up
b. Cable Internet Access, DSL, Dial-Up
c. WiMax, 3G, Wi-Fi
d. WiMax, DSL, Dial-up
Hide Answer ⟵









No comments:
Post a Comment